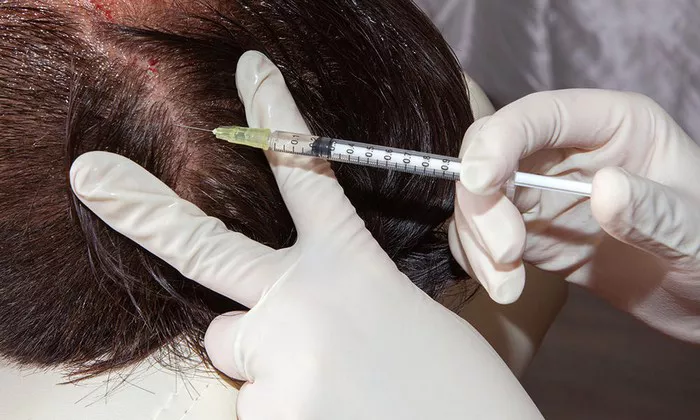
Hair transplant surgery has become a widely accepted solution for individuals experiencing hair loss. With advancements in technology and techniques, such as follicular unit transplantation (FUT) and follicular unit extraction (FUE), the procedure has become more effective and accessible. However, like any surgical procedure, hair transplants come with potential side effects. Understanding these side effects is crucial for anyone considering this treatment. This article will explore the common and rare side effects of hair transplants, how to manage them, and what to expect during the recovery process.
Understanding Hair Transplant Surgery
Before delving into the side effects, it’s important to understand what a hair transplant entails. The procedure involves extracting hair follicles from a donor area (typically the back or sides of the scalp) and implanting them into the recipient area (where hair loss has occurred). The two primary techniques used are:
Follicular Unit Transplantation (FUT): A strip of skin containing hair follicles is removed from the donor area, and the follicles are then transplanted into the recipient area.
Follicular Unit Extraction (FUE): Individual hair follicles are extracted directly from the donor area and implanted into the recipient area.
Both techniques are effective, but they differ in terms of invasiveness, recovery time, and potential side effects.
Common Side Effects of Hair Transplants
Most side effects of hair transplant surgery are temporary and subside within a few days or weeks. Below are the most commonly reported side effects:
1. Swelling
Swelling is a typical side effect, particularly in the forehead and around the eyes. It usually occurs within the first few days after the procedure and resolves on its own within a week. Keeping your head elevated and applying cold compresses can help reduce swelling.
2. Pain and Discomfort
Mild pain or discomfort in the donor and recipient areas is common after the surgery. This can usually be managed with over-the-counter pain relievers or medications prescribed by your surgeon.
3. Itching
Itching is a normal part of the healing process as the scalp begins to recover. However, scratching the affected area can damage the newly transplanted follicles. Your surgeon may recommend a topical solution or antihistamine to alleviate itching.
4. Scabbing and Crusting
Small scabs or crusts may form around the transplanted hair follicles. These are a natural part of the healing process and typically fall off within 7–10 days. It’s important not to pick at the scabs, as this can disrupt the healing process.
5. Numbness
Temporary numbness in the donor and recipient areas is common due to the disruption of nerve endings during the procedure. Sensation usually returns within a few weeks or months.
6. Shock Loss
Shock loss refers to the temporary shedding of existing hair in the recipient area. This occurs as a result of the trauma caused by the procedure. The shed hair typically regrows within a few months.
Rare Side Effects of Hair Transplants
While most side effects are mild and temporary, there are some rare but more serious complications that can occur. These include:
1. Infection
Although rare, infections can occur if proper post-operative care is not followed. Signs of infection include redness, warmth, pus, and increased pain. If you suspect an infection, contact your surgeon immediately.
2. Bleeding
Some bleeding is normal during and immediately after the procedure. However, excessive bleeding may occur in rare cases, particularly if the patient has a bleeding disorder or is taking blood-thinning medications.
3. Scarring
Scarring is more common with FUT, as it involves removing a strip of skin. However, skilled surgeons can minimize the appearance of scars. FUE typically results in less noticeable scarring, but improper technique can lead to visible dot-like scars.
4. Cysts
Small cysts may develop in the recipient area as a result of trapped debris or dead skin cells. These cysts are usually harmless and can be treated by your surgeon if they become bothersome.
5. Unnatural-Looking Results
In rare cases, the transplanted hair may grow in an unnatural pattern or direction. This is often the result of poor surgical technique or inadequate planning. Choosing an experienced surgeon can help avoid this issue.
6. Allergic Reactions
Although uncommon, some patients may experience an allergic reaction to the anesthesia or other medications used during the procedure. Inform your surgeon of any known allergies beforehand.
Managing Side Effects and Ensuring a Smooth Recovery
Proper post-operative care is essential for minimizing side effects and ensuring a successful recovery. Here are some tips to help you manage the side effects and promote healing:
Follow Your Surgeon’s Instructions: Your surgeon will provide detailed aftercare instructions, including how to clean the scalp, when to resume normal activities, and what medications to take. Adhering to these guidelines is crucial for a smooth recovery.
Avoid Touching or Scratching the Scalp: Touching or scratching the treated areas can disrupt the healing process and increase the risk of infection.
Protect Your Scalp from the Sun: Exposure to direct sunlight can cause irritation and damage to the healing scalp. Wear a hat or use sunscreen (once the scalp has healed) to protect the area.
Stay Hydrated and Maintain a Healthy Diet: Proper hydration and nutrition can support the healing process and promote hair growth.
Attend Follow-Up Appointments: Regular check-ups with your surgeon allow them to monitor your progress and address any concerns promptly.
Long-Term Considerations
While most side effects are temporary, it’s important to consider the long-term aspects of a hair transplant. The transplanted hair will typically begin to grow within 3–4 months, with full results visible after 12–18 months. However, it’s important to note that a hair transplant does not prevent further hair loss. Patients may need additional procedures or ongoing treatments, such as minoxidil or finasteride, to maintain their results.
Conclusion
Hair transplant surgery is a safe and effective solution for hair loss, but it is not without potential side effects. Common side effects, such as swelling, itching, and scabbing, are usually mild and temporary. Rare complications, such as infection or scarring, can occur but are often avoidable with proper care and an experienced surgeon.
If you’re considering a hair transplant, it’s essential to consult with a qualified professional who can assess your individual needs and provide personalized recommendations. By understanding the potential side effects and following post-operative care instructions, you can achieve a successful outcome and enjoy the benefits of a fuller head of hair.
Ultimately, the key to minimizing side effects and ensuring a positive experience lies in choosing a reputable clinic, adhering to aftercare guidelines, and maintaining realistic expectations. With the right approach, a hair transplant can be a life-changing procedure that restores not only your hair but also your confidence.
You Might Be Interested In:
- Is Hair Transplant Covered by Insurance?
- Is Hair Transplant Allowed in Islam?
- What Happens 10 Years After a Hair Transplant?