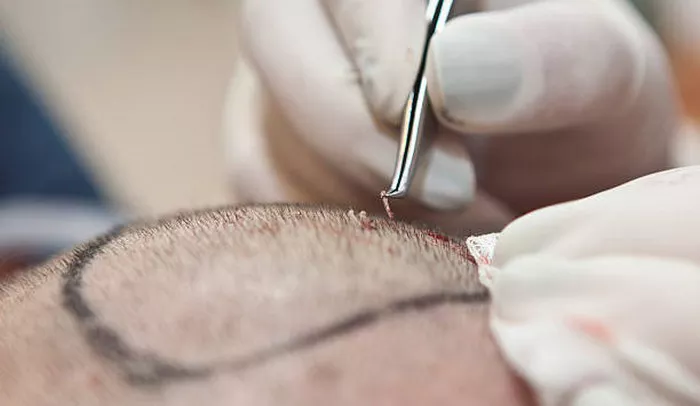
A hair transplant is a popular cosmetic procedure designed to restore hair to areas of the scalp where it has been lost. The process involves transferring hair follicles from one part of the body to another, and this procedure has been highly effective for individuals suffering from hair thinning or baldness. However, one common question among patients is: where exactly does the hair for a transplant come from? This article will explore the various sources of hair used in transplants, as well as the different types of hair transplants and their associated risks.
The Sources of Hair for Transplants
The primary source of hair for a transplant is the patient’s own scalp. This is known as autologous hair transplantation, where hair follicles are taken from areas of the scalp that are not affected by hair loss, such as the back or sides of the head, and then transplanted to the thinning or balding areas. In some cases, hair from other parts of the body, such as the chest or legs, can also be used. However, this is less common and typically occurs when there is not enough donor hair on the scalp.
While scalp hair is generally preferred for transplants, there are certain limitations, especially when a patient has extensive hair loss. This is where alternative methods such as body hair transplants may come into play, providing additional options for patients with limited donor hair available from their scalp.
Types of Hair Transplants
There are several different hair transplant types, each with its own unique approach and benefits. The two most commonly used methods are Follicular Unit Transplantation (FUT) and Follicular Unit Extraction (FUE). Below, we’ll dive into each technique and its advantages.
Follicular Unit Transplantation (FUT)
FUT involves removing a strip of scalp from the donor area (usually the back of the head), which is then dissected into individual follicular units. These units are transplanted into the balding areas. FUT can be ideal for patients who need a larger number of grafts because it allows the surgeon to harvest more hair in one go. However, this method often leaves a linear scar at the donor site, which may be noticeable if the hair is cut very short.
Follicular Unit Extraction (FUE)
FUE is a more modern technique where individual hair follicles are extracted directly from the donor area using a tiny punch tool. This method is less invasive and leaves no linear scar, making it a preferred option for many patients who want a more natural look. However, FUE can be time-consuming and may require multiple sessions to achieve the desired results.
Body Hair Transplantation (BHT)
In cases where scalp hair is insufficient, body hair transplants (BHT) may be considered. This technique involves using hair follicles from other parts of the body, such as the chest, abdomen, or legs, to restore hair on the scalp. While BHT can offer a viable solution for patients with limited scalp hair, the texture of body hair may differ from scalp hair, leading to a less natural appearance in some cases.
Risks Associated with Hair Transplants
Like any surgical procedure, hair transplant risks should be carefully considered before undergoing the procedure. Common risks include infection, bleeding, scarring, and graft failure. Additionally, some patients may experience shock loss, where the transplanted hair falls out temporarily before regrowing.
Infection and Bleeding
Infection is a potential risk following any surgical procedure, including hair transplants. To minimize the chances of infection, patients must follow the post-operative care instructions provided by their surgeon. Bleeding can also occur during the procedure or in the days following surgery, but it is usually manageable.
Scarring
Scarring is another concern, especially with the FUT method, which leaves a linear scar at the donor site. While FUE typically results in less noticeable scarring, tiny dots of scarring may still occur in the donor area.
Shock Loss
Shock loss refers to the shedding of both transplanted and native hair around the transplant site. This is a temporary condition that occurs as part of the healing process, and hair typically grows back after a few months. However, it is important to be aware of this possibility when considering a hair transplant.
Conclusion
Hair transplants offer a long-term solution for hair loss, allowing individuals to restore their hair and confidence. Understanding where the hair for transplants comes from, along with the different types of hair transplant methods and their potential risks, is crucial for anyone considering the procedure. By consulting with a qualified surgeon, patients can choose the best approach for their needs and ensure a successful outcome.
Related Topics
- 4 Methods To Hide My Head After Hair Transplant
- 4 Effects of Hair Transplantation on the Skin System
- 5 Best Hair Transplant Clinics In The World