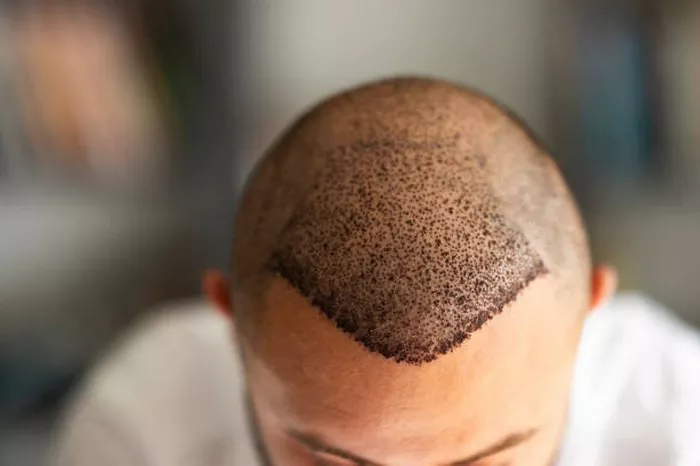
Male pattern baldness is a common issue that affects a significant number of men around the world. It can have a profound impact on a man’s self – esteem and confidence. Thankfully, hair transplant surgery has emerged as an effective solution to combat this problem. In this article, we will explore in detail how male hair transplant works, from the basic concepts to the actual procedures and after – care.
Understanding Male Pattern Baldness
Before delving into hair transplant procedures, it’s crucial to understand the root cause of male pattern baldness. Male pattern baldness, also known as androgenetic alopecia, is mainly caused by a combination of genetic factors and the hormone dihydrotestosterone (DHT). DHT is derived from testosterone, and in men with a genetic predisposition, it attaches to hair follicles in the scalp. This attachment gradually shrinks the follicles, leading to thinner and shorter hair growth over time. Eventually, the follicles may stop producing hair altogether, resulting in bald patches, typically starting at the temples and crown of the head.
The Basics of Hair Transplant
The fundamental principle behind hair transplant is the transplantation of hair follicles from one part of the body, usually the back or sides of the scalp (the donor area), to the bald or thinning areas (the recipient area). The hair follicles in the donor area are genetically resistant to the effects of DHT. This means that when they are transplanted to the recipient area, they will continue to grow hair as they did in their original location, regardless of the DHT levels in the new environment.
Follicular Unit Extraction (FUE)
Follicular Unit Identification
In the FUE method, the first step is to identify the follicular units. A follicular unit is a naturally occurring grouping of 1 – 4 hair follicles, along with their associated sebaceous glands, arrector pili muscles, and connective tissue. These units are carefully examined under a microscope or with the help of magnification tools.
The surgeon looks for healthy – looking follicular units in the donor area, which is typically the back and sides of the scalp. This area is chosen because the hair follicles here are less likely to be affected by male pattern baldness due to their genetic makeup.
Extraction Process
Once the follicular units are identified, a small, circular punch tool is used to extract them one by one. The diameter of the punch is usually between 0.7 – 1.2 mm, depending on the density of the hair and the size of the follicular units.
The extraction is a highly precise process. The surgeon must be careful not to damage the hair follicles during extraction. Local anesthesia is administered to the donor area to minimize pain during this step. The anesthetic numbs the area, allowing the patient to remain awake and comfortable throughout the extraction process.
After extraction, each follicular unit is immediately placed in a special solution that keeps it viable. This solution contains nutrients and substances that help maintain the health of the follicles until they are transplanted.
Preparation of the Recipient Area
While the extraction is taking place, the recipient area (the bald or thinning parts of the scalp) is also being prepared. The area is first cleaned and disinfected. Local anesthesia is then applied to the recipient area to ensure the patient does not feel pain during the implantation.
Using a very fine needle or a special implantation device, the surgeon creates tiny incisions in the recipient area. The size and direction of these incisions are carefully planned to mimic the natural growth pattern of hair. The incisions are made at an angle that is consistent with the natural hair growth direction in that particular area of the scalp, so that the transplanted hair will grow in a natural – looking manner.
Implantation
The extracted follicular units are then implanted into the incisions in the recipient area. The surgeon uses forceps or a specialized implantation tool to gently place each follicular unit into the incision. The depth of implantation is also carefully controlled to ensure that the follicles are placed at the correct level in the scalp for optimal growth.
The density of the implantation depends on the patient’s goals and the amount of available donor hair. In general, a higher density of implantation can create a fuller – looking result, but it also requires more donor hair. The surgeon will work with the patient to determine the best implantation density based on the patient’s hair characteristics and aesthetic goals.
Follicular Unit Transplantation (FUT)
Strip Harvesting
In the FUT method, the first step is strip harvesting. A strip of skin, usually about 1 – 2 centimeters wide and several centimeters long, is removed from the donor area, which is again the back or sides of the scalp. This strip contains a large number of hair follicles.
Local anesthesia is administered to the donor area to make the patient comfortable during the harvesting. The area is carefully marked before the incision is made. The incision is made with a scalpel, and the strip of skin is removed with precision. After the strip is removed, the wound in the donor area is closed with sutures or staples.
Dissection of Follicular Units
Once the strip is harvested, it is taken to a special laboratory where trained technicians carefully dissect it into individual follicular units. This is a very delicate process that requires a high level of skill and magnification. The technicians use fine – tipped surgical instruments to separate the follicular units while minimizing damage to the follicles.
The dissected follicular units are then placed in a nutrient – rich solution to keep them healthy until they are transplanted.
Preparation of the Recipient Area and Implantation
Similar to the FUE method, the recipient area is prepared by cleaning, disinfecting, and applying local anesthesia. Tiny incisions are made in the recipient area to receive the follicular units.
The dissected follicular units are then implanted into the incisions in the recipient area. The implantation process is also highly precise, with the surgeon carefully placing each follicular unit at the correct angle and depth to ensure natural – looking hair growth.
The Role of the Surgeon
The expertise of the surgeon plays a vital role in the success of a hair transplant. A skilled surgeon will have a deep understanding of the anatomy of the scalp and hair follicles. They will be able to accurately assess the amount of donor hair available, the appropriate transplantation method for the patient, and the best implantation density and pattern to achieve a natural – looking result.
During the procedure, the surgeon’s steady hand and attention to detail are crucial. Whether it’s the extraction of follicular units in FUE or the strip harvesting and implantation in FUT, any mistakes can lead to damage to the follicles, which may result in poor hair growth or an unnatural appearance. A good surgeon will also communicate effectively with the patient throughout the process, answering any questions and addressing concerns.
Post – operative Care
After the hair transplant surgery, proper post – operative care is essential for the success of the procedure.
Initial Recovery
Immediately after the surgery, the patient’s scalp will be covered with a dressing. The patient is usually advised to rest and avoid any strenuous activities for the first few days. Swelling is a common side effect, especially in the forehead and around the eyes. Cold compresses can be used to reduce swelling.
The patient will be prescribed medications, such as antibiotics to prevent infection and anti – inflammatory drugs to reduce swelling and discomfort. It’s important to take these medications as directed.
Scalp Care
The patient will be given instructions on how to clean the scalp. Gentle washing of the scalp is usually recommended starting a few days after the surgery. Special shampoos may be prescribed to keep the scalp clean and promote healing.
Avoiding scratching or rubbing the scalp is crucial, as this can dislodge the implanted follicles. The scabs that form around the implanted follicles should be allowed to fall off naturally.
Hair Growth and Follow – up
In the first few weeks after the surgery, the transplanted hair may fall out. This is a normal part of the process, as the hair follicles go through a resting phase before starting to grow new hair. New hair growth usually begins to appear around 3 – 6 months after the surgery, and it will continue to grow and thicken over the next 12 – 18 months.
Regular follow – up appointments with the surgeon are necessary to monitor the progress of hair growth and to ensure that there are no complications. The surgeon may adjust the treatment plan if needed based on the patient’s progress.
Advantages of Hair Transplant
Natural – looking Results
When performed by a skilled surgeon, a hair transplant can produce very natural – looking results. The transplanted hair will grow in the same direction as the natural hair, and the density can be adjusted to match the patient’s existing hair.
Permanent Solution
Since the transplanted hair follicles are taken from areas that are resistant to DHT, the new hair growth is permanent. Once the transplanted hair follicles are established in the recipient area, they will continue to grow hair for the rest of the patient’s life.
Boost in Self – esteem
For many men, regaining a full head of hair through a hair transplant can have a significant positive impact on their self – esteem and confidence. It can improve their overall quality of life and how they perceive themselves.
Risks and Considerations
Infection
Although rare, there is a risk of infection at the donor and recipient sites. Following proper post – operative care, including taking antibiotics as prescribed, can minimize this risk.
Scarring
In the FUT method, there will be a linear scar in the donor area where the strip of skin was removed. However, with proper suturing techniques and scar management, this scar can be made less visible. In the FUE method, the individual puncture marks from the extraction may leave small scars, but these are usually less noticeable.
Unnatural Appearance
If the hair transplant is not performed properly, the result may look unnatural. This can be due to incorrect implantation angles, improper density, or damage to the follicles during the procedure. Choosing an experienced and reputable surgeon is the best way to avoid this risk.
Conclusion
Male hair transplant is a complex but highly effective procedure for treating male pattern baldness. By understanding how it works, from the causes of hair loss to the different transplantation methods and post – operative care, men can make an informed decision about whether a hair transplant is the right option for them. With the right surgeon and proper care, a hair transplant can provide a natural – looking, permanent solution to hair loss, helping men regain their confidence and a full head of hair.
Related topics:
How Long To Stay In Turkey After Hair Transplant?
Use Of Biotin Before Hair Transplantation: Reasons, Benefits & Side Effects