Hair transplant surgery has become an increasingly popular solution for those suffering from hair loss. While the procedure itself is a significant step towards regaining confidence, understanding the various aspects of the surgery, including the anesthesia used, is crucial for patients. One common question that arises is, “How Long Does Anesthesia Last After Hair Transplant?” In this article, we will explore this topic in detail, covering everything from the types of anesthesia used in hair transplant procedures to the factors that can influence the duration of its effects.
Types of Anesthesia Used in Hair Transplant
Local Anesthesia
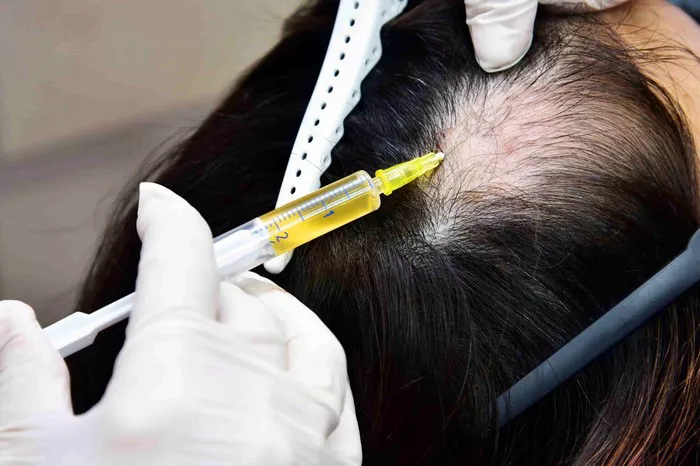
Local anesthesia is the most commonly used type of anesthesia in hair transplant surgery. It numbs only the specific area where the procedure is being performed, which in this case is the scalp. This allows the patient to remain awake during the surgery while feeling minimal to no pain. Local anesthesia works by blocking the nerve signals from the area being numbed, preventing the brain from receiving pain messages.
The local anesthetic is typically injected directly into the scalp. The injection may cause a brief stinging or burning sensation, but this quickly subsides as the anesthetic takes effect. Once the anesthetic is in place, the surgeon can begin the hair transplant procedure. The duration of local anesthesia can vary, but generally, it starts to take effect within a few minutes of injection.
General Anesthesia
Although less common in hair transplant surgery, some patients may opt for general anesthesia. General anesthesia puts the patient into a deep sleep, meaning they are unconscious during the entire procedure. This is usually reserved for patients who have a high level of anxiety about the surgery or for more complex transplant cases.
General anesthesia is administered through an intravenous (IV) line or inhalation. The patient is carefully monitored throughout the procedure by an anesthesiologist to ensure their vital signs remain stable. Once the surgery is complete, the anesthesiologist will gradually reduce the amount of anesthesia being administered, and the patient will start to wake up. However, the recovery time from general anesthesia is typically longer compared to local anesthesia.
Factors Affecting the Duration of Anesthesia
Type of Anesthetic Used
The type of anesthetic plays a significant role in how long the anesthesia will last. Different local anesthetics have different durations of action. For example, lidocaine is a commonly used local anesthetic in hair transplant procedures. When used alone, lidocaine typically provides numbness for about 1 to 2 hours. However, when combined with epinephrine, which is a vasoconstrictor, the duration of action can be extended to 3 to 5 hours. Epinephrine works by constricting the blood vessels in the area, which slows down the absorption of the anesthetic, thus prolonging its effect.
In the case of general anesthesia, different medications are used, and their durations of action vary as well. Some general anesthetics are short – acting and are designed to wear off quickly, allowing the patient to wake up soon after the surgery. Others are longer – acting and may require additional measures to reverse their effects or a longer recovery time.
Dosage of Anesthetic
The amount of anesthetic administered also affects how long it will last. A higher dosage of local anesthetic will generally provide numbness for a longer period. However, the dosage is carefully calculated by the surgeon or anesthesiologist based on several factors, including the size of the area to be numbed, the patient’s weight, and overall health. Giving too much anesthesia can lead to potential side effects, so it’s essential to find the right balance.
For general anesthesia, the dosage is also precisely controlled. The anesthesiologist will adjust the amount of anesthesia based on the length of the surgery and the patient’s response. If the surgery takes longer than expected, additional anesthesia may be administered to keep the patient unconscious.
Patient’s Metabolism
A patient’s metabolism can have a significant impact on how long the anesthesia lasts. Metabolism refers to the body’s process of breaking down and eliminating substances, including anesthetics. Patients with a faster metabolism will generally process the anesthetic more quickly, causing it to wear off sooner. On the other hand, patients with a slower metabolism may experience the effects of the anesthesia for a longer time.
Factors that can affect metabolism include age, body weight, and certain medical conditions. For example, older patients tend to have a slower metabolism compared to younger patients. Obesity can also affect metabolism, as adipose tissue can store anesthetics, releasing them slowly over time. Medical conditions such as thyroid disorders can also impact metabolism and, consequently, the duration of anesthesia.
Area of the Body Being Anesthetized
In hair transplant surgery, the scalp is the area being anesthetized. The scalp has a rich blood supply, which can affect the absorption and duration of the anesthetic. The blood vessels in the scalp can quickly carry the anesthetic away from the injection site, potentially shortening its duration of action. However, as mentioned earlier, the use of vasoconstrictors like epinephrine can counteract this effect.
Compared to other areas of the body, the scalp may have a slightly different response to anesthesia. For example, the skin on the scalp is relatively thick, which may require a slightly higher volume of anesthetic to achieve the desired level of numbness. Additionally, the presence of hair follicles and the underlying muscles and connective tissues can also influence how the anesthetic spreads and is absorbed.
Duration of Anesthesia Effects
Immediate Post – Surgery
Immediately after the hair transplant surgery, if local anesthesia was used, the area of the scalp where the surgery was performed will still be numb. This numbness can last anywhere from a few hours to several hours, depending on the factors mentioned above. Patients may notice that they can’t feel any pain in the area, and there may also be a tingling or “pins and needles” sensation as the anesthesia starts to wear off.
If general anesthesia was used, the patient will wake up in the recovery room. Initially, they may feel groggy, confused, and have difficulty focusing. Their speech may be slurred, and they may have trouble moving their limbs smoothly. This is a normal part of the recovery process from general anesthesia, and these effects will gradually subside over time.
First Day After Surgery
On the first day after hair transplant surgery, if local anesthesia was used, the numbness in the scalp should start to fade significantly. However, the area may still be tender and sensitive. Patients may experience some mild pain or discomfort, which can usually be managed with over – the – counter pain relievers as recommended by their surgeon.
For patients who had general anesthesia, they may still feel some residual effects on the first day. They may be tired, have a headache, or feel nauseous. It’s important for these patients to rest and follow the post – operative instructions carefully. They should also avoid driving or operating heavy machinery on the first day after surgery due to the potential for impaired judgment and coordination.
Long – Term Effects
In most cases, there are no long – term effects of the anesthesia used in hair transplant surgery. Once the anesthesia has completely worn off, the body returns to its normal state. However, in rare cases, some patients may experience minor complications related to the anesthesia.
For local anesthesia, there is a small risk of developing an allergic reaction to the anesthetic. Symptoms of an allergic reaction can include itching, swelling, rash, or difficulty breathing. If a patient experiences any of these symptoms, they should seek medical attention immediately. Another potential complication is nerve damage from the injection. Although this is extremely rare, it can cause persistent numbness or tingling in the scalp.
With general anesthesia, there is a slightly higher risk of complications. These can include more severe allergic reactions, problems with the airway during the administration of anesthesia, and long – term cognitive effects. However, these risks are relatively low, especially when the procedure is performed by experienced medical professionals in a well – equipped facility.
Recovery and Aftercare
Managing Discomfort
As the anesthesia wears off, patients will start to experience some discomfort. This is normal and part of the healing process. To manage the discomfort, patients can take the pain medications prescribed by their surgeon. Over – the – counter pain relievers like acetaminophen can be effective for mild to moderate pain. In some cases, the surgeon may prescribe stronger pain medications, but these are usually reserved for more severe pain.
Applying a cold compress to the scalp can also help reduce swelling and discomfort. Patients should be careful not to apply the cold compress directly to the surgical area but rather to the surrounding areas. It’s important to follow the surgeon’s instructions on how often and for how long to apply the cold compress.
Monitoring for Complications
Patients need to closely monitor the surgical area for any signs of complications. This includes looking for excessive bleeding, swelling that is not subsiding, redness, or signs of infection such as pus or a foul smell. If any of these symptoms are present, patients should contact their surgeon immediately.
For patients who had general anesthesia, they should also be aware of any changes in their overall health, such as persistent nausea, vomiting, or difficulty breathing. These could be signs of a more serious complication related to the anesthesia.
Follow – Up Appointments
Follow – up appointments with the surgeon are an essential part of the recovery process. During these appointments, the surgeon will check the progress of the hair transplant, assess the healing of the scalp, and answer any questions the patient may have. The surgeon may also provide additional instructions on aftercare, such as when it’s safe to start washing the hair or resuming normal activities.
Conclusion
The duration of anesthesia after a hair transplant depends on several factors, including the type of anesthesia used, the dosage, the patient’s metabolism, and the area being anesthetized. Understanding these factors can help patients better prepare for the surgery and manage their expectations during the recovery process. By following the surgeon’s instructions for aftercare and monitoring for any complications, patients can ensure a smooth recovery and the best possible outcome from their hair transplant procedure.
Related topics:
5 Simple Treatments After A Club Hair Transplant