Hair transplant surgery has become a popular solution for those struggling with hair loss. While the focus is often on the growth of new hair, understanding the healing process of the scars left behind is equally important. The time it takes for a hair transplant scar to heal can vary based on several factors, including the surgical technique used, individual healing abilities, and post – operative care. This article will explore in detail how long hair transplant scars take to heal and what you can do to promote optimal healing.
Types of Hair Transplant Techniques and Their Scarring
Follicular Unit Transplantation (FUT)
Surgical Process
Follicular Unit Transplantation, also known as the strip method, involves removing a strip of skin from the donor area, usually the back of the head. This strip contains multiple hair follicles. The strip is then dissected in a laboratory into individual follicular units, which are transplanted into the recipient area (the bald or thinning part of the scalp).
Scar Appearance and Initial Healing
The scar left by FUT is a linear scar along the area where the strip was removed. In the immediate post – operative period, the scar will be covered with a dressing. After the dressing is removed, usually within a few days, the scar will appear as a red, raw line. The initial healing process begins with the formation of a scab over the incision. This scab helps protect the underlying tissue as it starts to repair.
The scab typically forms within 1 – 2 days after the surgery. In the first week, the body starts to close the wound by forming new tissue. The edges of the incision gradually come together, and the scab starts to harden. During this time, it’s important not to pick at the scab, as this can disrupt the healing process and increase the risk of infection and scarring.
Long – Term Scar Development
Over the next few weeks, the scab will gradually fall off, usually around 7 – 10 days after the surgery. Once the scab is gone, the scar will be pink and raised. This is a normal part of the healing process as the body continues to produce collagen to strengthen the new tissue.
As the weeks progress, the scar will start to fade. By 2 – 3 months, the scar will become less red and start to blend in with the surrounding skin. However, it may still be visible, especially in people with light – colored hair or when the hair is cut very short. In some cases, it can take up to 6 – 12 months for the scar to fully mature and become as inconspicuous as possible. With proper care and in some cases, additional scar – management techniques, the visibility of the FUT scar can be minimized.
Follicular Unit Extraction (FUE)
Surgical Process
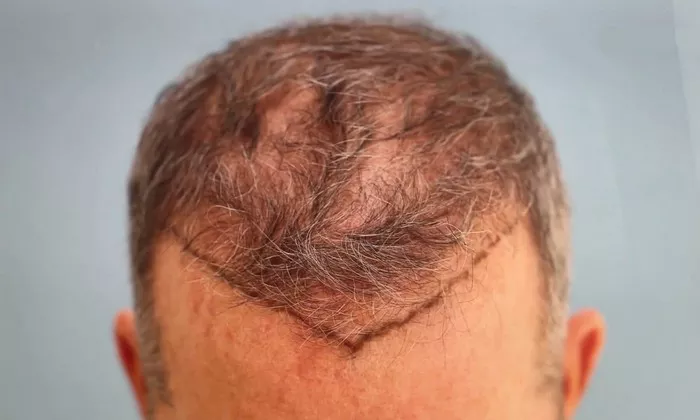
Follicular Unit Extraction is a different approach. Instead of removing a strip of skin, individual follicular units are extracted directly from the donor area using a small punch tool. These units are then transplanted into the recipient area. This method is often preferred by patients who want to avoid a linear scar.
Scar Appearance and Initial Healing
The scars left by FUE are small, circular dots at the sites where the follicles were extracted. In the first few days after the surgery, these small incisions will be covered with a thin layer of scabs. The scabs are much smaller compared to the scab in FUT.
The initial healing of these small incisions is relatively quick. The scabs usually start to form within the first 24 – 48 hours. In the first week, the body begins to heal the tiny wounds, and the scabs start to dry out. Similar to FUT, it’s crucial not to disturb the scabs during this time.
Long – Term Scar Development
By the end of the first week, most of the scabs in FUE will have fallen off. The small scars will appear as tiny pink dots. Over the next few weeks, these dots will start to fade. Since the scars are small and spread out, they are generally less noticeable than the linear scar in FUT.
Within 1 – 2 months, the FUE scars will become even less visible as the skin around the scars continues to heal and the hair starts to grow back in the donor area. In many cases, the FUE scars become almost invisible, especially when the hair is of a normal length, as the growing hair helps to conceal them. However, in some individuals with very short – cropped hair or those with lighter – colored hair, the scars may still be faintly visible, but much less so than a FUT scar.
Factors Affecting Scar Healing
Individual Healing Abilities
Everyone’s body heals at a different rate. Some people have a more efficient healing process due to factors such as a strong immune system, good overall health, and genetic factors. For example, younger patients generally tend to heal faster than older patients. A person with a healthy lifestyle, including a balanced diet, regular exercise, and sufficient sleep, is more likely to have a quicker and smoother scar – healing process.
On the other hand, individuals with certain medical conditions like diabetes, which can affect blood circulation and the body’s ability to repair tissue, may experience slower scar healing. People taking medications that suppress the immune system, such as those undergoing chemotherapy or taking immunosuppressive drugs after an organ transplant, may also have a more challenging time healing from hair transplant scars.
Post – operative Care
Proper post – operative care plays a vital role in scar healing. Keeping the surgical area clean is essential. This means gently washing the scalp with a mild, doctor – recommended shampoo. Avoiding harsh chemicals and excessive scrubbing can prevent irritation and damage to the healing scar.
Following the doctor’s instructions regarding the use of any topical ointments or medications is also crucial. Some doctors may prescribe antibiotic ointments to prevent infection, which can significantly delay the healing process. Additionally, protecting the scar from sunlight is important. UV rays can damage the new skin tissue and cause the scar to become darker and more prominent. Wearing a hat when outdoors can help shield the scar from the sun.
Surgical Technique and Surgeon’s Skill
The skill of the surgeon performing the hair transplant also affects scar healing. A more experienced surgeon is more likely to make precise incisions, whether in FUT or FUE. In FUT, a skilled surgeon can ensure that the strip is removed and the incision is closed neatly, reducing the risk of uneven scarring.
In FUE, a proficient surgeon can extract the follicles with minimal damage to the surrounding tissue. This results in smaller and less noticeable scars. The surgical technique used can also impact the amount of trauma to the skin, which in turn affects the healing time and the final appearance of the scar.
Scar Management Techniques
Topical Treatments
There are several topical treatments that can help improve the appearance of hair transplant scars. Silicone – based gels or sheets are commonly used. These products work by creating a protective barrier over the scar, which helps to keep the scar hydrated and flat. They can also reduce the production of excess collagen, which can cause the scar to become raised.
Vitamin E oil is another option. It is believed to have antioxidant properties that can promote skin healing and reduce the appearance of scars. However, it’s important to note that some people may be allergic to vitamin E, so it’s advisable to do a patch test on a small area of skin before applying it to the scar.
Laser Therapy
Laser therapy can be an effective option for reducing the appearance of hair transplant scars, especially for more stubborn or prominent scars. Laser treatment works by targeting the scar tissue with light energy. This stimulates the production of new collagen and elastin in the skin, which can help to smooth and fade the scar.
There are different types of lasers that can be used, such as fractional lasers and pulsed – dye lasers. The number of laser treatments required depends on the severity of the scar and the individual’s response to the treatment. Laser therapy is usually done a few months after the hair transplant surgery, once the scar has had time to heal to a certain extent.
Microneedling
Microneedling is a minimally invasive procedure that involves using a device with fine needles to create tiny punctures in the skin. This stimulates the body’s natural healing response, promoting the production of collagen and elastin. When applied to hair transplant scars, microneedling can help to improve the texture and appearance of the scar.
Microneedling can be done in a series of sessions, usually spaced a few weeks apart. It’s important to have the procedure performed by a trained professional to ensure safety and effectiveness. In some cases, microneedling may be combined with other treatments, such as topical medications or platelet – rich plasma (PRP) therapy, to enhance the results.
Psychological Impact of Scar Healing
Anxiety During the Healing Process
The process of waiting for a hair transplant scar to heal can be a source of anxiety for many patients. In the early stages, when the scar is most visible, patients may feel self – conscious, especially if they are in a social or professional environment where their appearance is important.
For example, a person who has a high – profile job or is very active in social circles may worry about how the scar will be perceived by others. This anxiety can be compounded if the healing process seems to be taking longer than expected or if there are signs of abnormal scarring, such as excessive redness or itching.
Coping Strategies
To cope with the anxiety, it’s important for patients to have realistic expectations about the scar – healing process. Understanding that scar healing is a gradual process and that it takes time for the scar to fade can help reduce anxiety. Communicating with the surgeon or a support group of other hair transplant patients can also provide emotional support.
Some patients find it helpful to focus on other aspects of their recovery, such as the growth of new hair. Taking care of their overall health, including getting enough sleep, eating well, and exercising, can also have a positive impact on their mental state during the scar – healing process.
Conclusion
The time it takes for a hair transplant scar to heal depends on multiple factors, including the surgical technique (FUT or FUE), individual healing abilities, and post – operative care. FUT scars generally take longer to heal and may be more visible in the long – term compared to FUE scars. However, with proper care and the use of scar – management techniques, the appearance of both types of scars can be significantly improved.
The psychological impact of scar healing should not be overlooked. Patients should be prepared for the emotional challenges that may come with waiting for the scar to fade and should seek support when needed. By understanding the scar – healing process and taking proactive steps to care for the scar, patients can achieve the best possible outcome from their hair transplant surgery.
Related topics:
What Is The Price Of Automated Hair Transplant System?