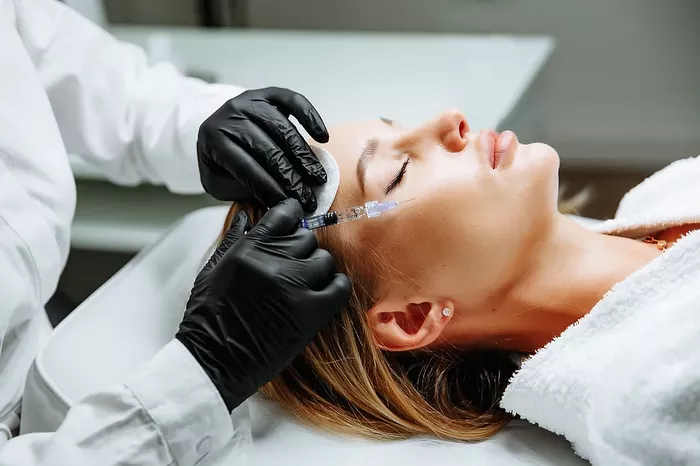
Hair transplants have become a popular solution for those struggling with hair loss. Whether it’s due to male – pattern baldness, female – pattern hair loss, or other factors, the prospect of regaining a full head of hair is appealing. However, before diving into a hair transplant procedure, there are several crucial things you should be aware of. This article will cover six important aspects that every person considering a hair transplant should know.
1. The Different Types of Hair Transplant Techniques
Follicular Unit Transplantation (FUT)
The Procedure
Follicular Unit Transplantation, often called the strip method, is one of the oldest and most well – established hair transplant techniques. During this procedure, the surgeon removes a strip of skin from the back or sides of the head, which is known as the donor area. This area is chosen because the hair follicles there are genetically resistant to balding.
How It Works
Once the strip is removed, the wound in the donor area is sutured closed. The strip is then dissected in a laboratory into individual follicular units, which are groups of 1 – 4 hairs. These follicular units are then carefully implanted into tiny incisions made in the recipient area (the balding or thinning part of the scalp) using specialized instruments.
Advantages and Disadvantages
One of the main advantages of FUT is that it can harvest a large number of follicular units in one session, making it suitable for those with significant hair loss. It also generally provides a more natural – looking hairline. However, the donor area may leave a linear scar, which can be visible, especially in people with short hair. The recovery time for the donor area can also be longer compared to other techniques.
Follicular Unit Extraction (FUE)
The Procedure
Follicular Unit Extraction is a more modern hair transplant technique. Instead of removing a strip of skin, individual follicular units are extracted directly from the donor area using a small, circular punch tool. These punches are usually very fine, ranging from 0.6 – 1.0 mm in diameter.
How It Works
The extracted follicular units are then immediately implanted into the recipient area. This technique is less invasive as it doesn’t require a large incision in the donor area. The individual extraction sites in the donor area heal as small dots, and over time, they become less noticeable.
Advantages and Disadvantages
The main advantage of FUE is that it leaves minimal scarring in the donor area, making it a great option for those who want to keep their hair short. The recovery time for the donor area is also relatively short. However, FUE can be more time – consuming, especially for large – scale transplants, as each follicular unit is extracted individually. It may also be more expensive due to the higher level of skill and precision required.
Other Techniques
Direct Hair Implantation (DHI)
Direct Hair Implantation is a variation of FUE. In DHI, the extracted follicular units are immediately implanted into the recipient area using a special pen – like device. This is claimed to reduce the time the follicles are out of the body, potentially increasing their survival rate. It also allows for more precise placement of the follicles, which can lead to a more natural – looking result. However, like FUE, it can be time – consuming and may require a highly skilled surgeon.
2. The Importance of a Qualified Surgeon
Experience Matters
Proven Track Record
When choosing a hair transplant surgeon, experience is key. A surgeon who has performed a large number of hair transplant procedures is more likely to have encountered various hair loss situations and anatomical variations. They will have developed the skills and techniques necessary to achieve good results. Look for a surgeon who has been performing hair transplants for at least 5 – 10 years and has a portfolio of successful cases.
Avoiding Complications
An experienced surgeon is better equipped to handle any complications that may arise during the procedure. For example, if there is excessive bleeding, a skilled surgeon will know how to manage it quickly and effectively. They are also more likely to avoid common mistakes, such as improper placement of follicles, which can lead to an unnatural – looking hairline or poor hair growth.
Board Certification
What It Means
Board certification is an important indicator of a surgeon’s qualifications. In the field of hair transplantation, board – certified surgeons have met specific educational, training, and examination requirements. For example, in the United States, the American Board of Hair Restoration Surgery (ABHRS) provides certification for hair transplant surgeons. Board – certified surgeons are more likely to follow ethical and professional standards, ensuring that you receive high – quality care.
Ensuring Quality Care
When you choose a board – certified surgeon, you can have more confidence in the safety and effectiveness of the procedure. They are required to stay updated with the latest advancements in hair transplant techniques and research, which means you are more likely to benefit from the most current and proven methods.
3. The Pre – Transplant Evaluation
Medical History
Underlying Conditions
Your medical history plays a crucial role in determining your suitability for a hair transplant. Conditions such as diabetes, high blood pressure, heart disease, and autoimmune disorders can affect the outcome of the surgery. For example, diabetes can slow down the healing process, increasing the risk of infection. Your surgeon will need to know about any pre – existing medical conditions so that they can take appropriate precautions or may even recommend against the surgery if it’s too risky.
Medication Use
Certain medications can also impact the hair transplant. Blood – thinning medications, for example, can increase the risk of bleeding during the procedure. If you’re taking any prescription or over – the – counter medications, including supplements, it’s important to inform your surgeon. They may ask you to stop taking certain medications for a period before the surgery to reduce the risk of complications.
Hair Loss Pattern and Scalp Condition
Evaluating the Extent of Hair Loss
The pattern and extent of your hair loss will help the surgeon plan the transplant. If you have male – pattern baldness, the surgeon will need to assess the stage of the balding process to determine how many follicular units are needed and where to place them for the best aesthetic result. In some cases, a more advanced stage of hair loss may require multiple transplant sessions.
Scalp Health
The condition of your scalp is also important. A healthy scalp provides a better environment for the transplanted follicles to grow. If you have scalp conditions such as psoriasis, eczema, or seborrheic dermatitis, these need to be treated before the transplant. Otherwise, they can interfere with the healing process and the growth of the transplanted hair.
4. The Post – Transplant Recovery Process
Initial Recovery (0 – 2 Weeks)
Scalp Care
In the first few days after the transplant, the scalp will be tender and may be covered with a bandage. You’ll need to keep the scalp clean and follow the surgeon’s instructions on how to clean the area. Usually, this involves gently washing the scalp with a mild, antibacterial shampoo. Avoid scratching or rubbing the scalp, as this can dislodge the newly implanted follicles.
Swelling and Bruising
Swelling and bruising are common in the initial recovery phase. Swelling may be more prominent around the forehead and eyes, and it can take a few days to a week to subside. Bruising may also occur in the donor and recipient areas and can take 1 – 2 weeks to fade. Cold compresses can be used to reduce swelling, but be careful not to apply too much pressure on the scalp.
Intermediate Recovery (2 – 12 Weeks)
Hair Shedding
Around 2 – 3 weeks after the transplant, you may notice that the transplanted hair starts to shed. This is normal and is called “shock loss.” The hair follicles are adjusting to their new environment, and the existing hair shafts may fall out. But don’t worry, the follicles are still alive and will start to grow new hair in the coming weeks.
Avoiding Strenuous Activity
During this period, it’s important to avoid strenuous activities such as heavy exercise, weightlifting, and contact sports. These activities can increase blood flow to the scalp, which may cause bleeding or dislodge the follicles. Light walking and gentle stretching are usually okay, but consult your surgeon for specific advice.
Long – Term Recovery (12 Weeks – 1 Year)
Hair Growth
After about 12 weeks, you should start to see the first signs of new hair growth. The new hair will initially be fine and soft, but over time, it will thicken and become more like your natural hair. By 6 – 9 months, you should notice a significant improvement in hair density, and by 1 year, the full results of the transplant should be visible.
Follow – Up Appointments
Regular follow – up appointments with your surgeon are essential during the long – term recovery. They will monitor the growth of the transplanted hair, check for any complications, and may provide additional advice on hair care or medications to support hair growth.
5. The Cost of Hair Transplants
Factors Affecting Cost
Technique Used
As mentioned earlier, different hair transplant techniques have different costs. FUE, being a more precise and less invasive technique, is generally more expensive than FUT. The cost can also vary depending on the specific variation of the technique, such as DHI, which may be priced higher due to the specialized equipment and skills required.
Number of Follicular Units
The number of follicular units needed for the transplant is a major factor in determining the cost. If you have extensive hair loss and require a large number of follicular units to achieve a satisfactory result, the cost will be higher. The cost is often calculated per follicular unit, and the price per unit can vary depending on the clinic and the technique.
Geographical Location
The location of the hair transplant clinic can also impact the cost. Clinics in major cities or areas with a higher cost of living may charge more. Additionally, different regions may have different market rates for hair transplant procedures.
Hidden Costs
Pre – and Post – Operative Medications
There may be costs associated with pre – and post – operative medications. You may need to take antibiotics to prevent infection, painkillers to manage discomfort, and in some cases, medications like minoxidil or finasteride to support hair growth. These medications can add to the overall cost of the procedure.
Follow – Up Appointments
Some clinics may charge for follow – up appointments, especially if they are extensive or require additional tests. Make sure you understand what is included in the initial cost of the hair transplant and what additional costs you may incur during the follow – up period.
6. The Long – Term Outlook and Maintenance
Natural Aging and Hair Loss
Progression of Hair Loss
Even after a successful hair transplant, natural aging can still cause hair loss. The transplanted hair follicles are resistant to the hormones that cause male – or female – pattern baldness, but other factors such as genetic predisposition, stress, and hormonal changes can still affect the non – transplanted hair. You may need to continue to monitor your hair and consider additional treatments in the future to maintain the appearance of a full head of hair.
Hormonal Changes
Hormonal changes, such as those that occur during menopause in women or as a result of certain medical conditions, can impact hair growth. It’s important to be aware of these potential changes and discuss them with your surgeon. They may recommend lifestyle changes, medications, or other treatments to help manage hair loss associated with hormonal changes.
Maintenance of Transplanted Hair
Hair Care Routine
Maintaining a good hair care routine is essential for the long – term health of the transplanted hair. Use a gentle, sulfate – free shampoo to keep the scalp clean and the hair hydrated. Avoid using excessive heat styling tools, as they can damage the hair. Regular trims can also help keep the hair looking neat and healthy.
Medication and Supplements
In some cases, your surgeon may recommend continuing to use medications like minoxidil or finasteride to support the growth of the transplanted hair and prevent further hair loss. There are also supplements available that claim to promote hair health, but it’s important to consult your surgeon before starting any new supplements to ensure they are safe and effective.
Conclusion
Hair transplants can be a life – changing solution for those dealing with hair loss. However, it’s important to be well – informed before making the decision. By understanding the different types of techniques, the importance of a qualified surgeon, the pre – and post – transplant processes, the cost, and the long – term outlook, you can make a more informed choice. Remember to have open and honest discussions with your surgeon, ask plenty of questions, and do your research to ensure that your hair transplant journey is a successful one.
Related topics: