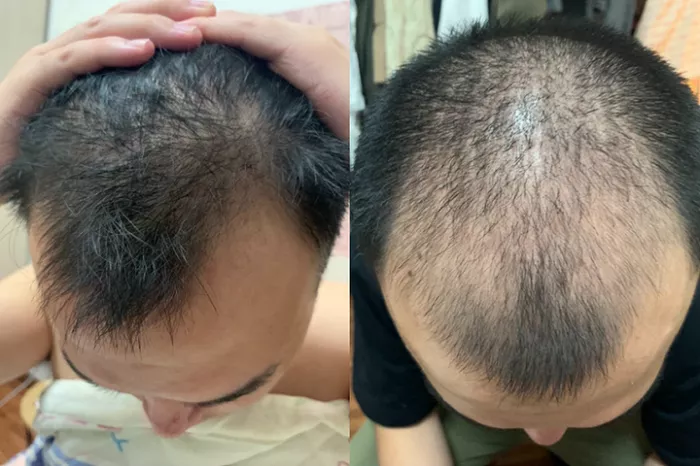
Hair transplantation has become an increasingly popular solution for individuals experiencing hair loss, particularly among students and professionals in the global education sector who seek to enhance their appearance for academic and career opportunities. However, one common side effect that patients encounter is post-operative swelling, which can cause discomfort and concern. This article delves into the physiological causes of swelling, its expected progression, effective management strategies, and preventive measures to ensure a smooth recovery process.
The Biological Mechanism Behind Swelling After Hair Transplant
Swelling following a hair transplant is a natural inflammatory response triggered by the body’s healing process. The key factors contributing to this phenomenon include:
Trauma to the Scalp: Follicular Unit Extraction (FUE) or Follicular Unit Transplantation (FUT) involves extracting and implanting hair grafts, which disrupts blood vessels and tissues, leading to localized fluid accumulation.
Increased Blood Flow: The body directs more blood to the treated area to deliver nutrients and immune cells, causing temporary edema.
Lymphatic System Response: The lymphatic drainage system may temporarily struggle to remove excess interstitial fluid, particularly if the patient remains sedentary post-surgery.
Understanding these mechanisms helps patients recognize that swelling is a normal, transient phase rather than a complication.
Timeline of Post-Transplant Swelling
Swelling typically follows a predictable pattern:
First 24–48 Hours: Mild swelling around the forehead and temples due to gravity pulling fluids downward.
Days 3–5: Peak swelling, often extending to the eyes and cheeks, giving a “puffy” appearance.
Days 6–7: Gradual reduction as the lymphatic system improves fluid drainage.
Week 2: Most swelling subsides, though minor residual puffiness may persist in some patients.
Patients should avoid panic if swelling worsens initially, as this is part of the natural healing trajectory.
Factors That Exacerbate Swelling After Hair Transplant
Certain behaviors and conditions can intensify post-operative edema:
Poor Head Elevation: Lying flat increases fluid retention in facial tissues.
Excessive Physical Activity: Strenuous exercise raises blood pressure, worsening swelling.
High Sodium Intake: Salty foods promote water retention.
Alcohol and Smoking: Both impair circulation and delay healing.
Touching or Rubbing the Scalp: This can irritate the grafts and increase inflammation.
Awareness of these factors enables patients to minimize unnecessary swelling through disciplined aftercare.
Effective Strategies to Reduce Swelling
To accelerate recovery, patients should adopt the following measures:
Proper Head Positioning
- Sleep at a 45-degree angle for the first 3–4 nights to facilitate fluid drainage.
- Use a travel neck pillow to avoid pressure on grafts.
Cold Compress Application
- Applyice packs wrapped in cloth (never directly on skin) to the forehead in intervals (20 minutes on, 20 minutes off).
- Avoid icing the transplanted area to prevent graft damage.
Medications and Topical Treatments
- Take prescribed anti-inflammatory drugs (e.g., corticosteroids) if recommended by the surgeon.
- Use aromatic oils (e.g., peppermint) to improve circulation once cleared by the doctor.
Hydration and Diet Adjustments
- Drink plenty of water to flush out toxins.
- Consume pineapple or bromelain supplements, which have natural anti-inflammatory properties.
When Should Swelling Be a Concern?
While swelling is normal, certain symptoms warrant medical attention:
Severe, Asymmetrical Swelling: Could indicate an allergic reaction or infection.
Persistent Swelling Beyond 10 Days: May suggest poor lymphatic drainage or other complications.
Accompanied by Fever or Pus: Signs of infection requiring antibiotics.
Patients should consult their surgeon immediately if these red flags appear.
Preventive Measures Before and After Surgery
Proactive steps can significantly reduce post-transplant swelling:
Pre-Surgery Preparations
- Avoid blood-thinning medications (e.g., aspirin, ibuprofen) for at least one week before the procedure.
- Refrain from alcohol and smoking 2–3 weeks prior to enhance blood flow and healing.
Post-Surgery Care
- Follow the surgeon’s aftercare instructions meticulously.
- Engage in light walking (after 48 hours) to stimulate lymphatic drainage.
Long-Term Implications of Swelling and How It Affects Graft Survival
While post-operative swelling is temporary, some patients worry about its potential impact on graft survival and long-term results. It’s important to clarify that properly managed swelling does not harm transplanted follicles, as the grafts are securely anchored within the scalp. However, excessive or prolonged swelling could indirectly affect outcomes by:
Delaying Nutrient Supply: Severe edema may temporarily reduce blood circulation to the grafts, slightly slowing initial healing.
Increasing Discomfort: Excessive swelling can lead to unnecessary touching or rubbing, which may dislodge grafts if done aggressively.
Affecting Post-Op Care Compliance: Patients experiencing significant swelling might neglect aftercare routines, such as gentle washing or prescribed medications.
To mitigate these risks, surgeons often recommend:
- Gentle Massage Techniques (after the first week) to encourage lymphatic drainage without disturbing grafts.
- Low-Level Laser Therapy (LLLT), which can reduce inflammation while promoting follicle health.
- Regular Follow-Ups to monitor healing progress and adjust aftercare if needed.
Studies indicate that patients who follow structured recovery protocols experience minimal impact on graft survival, even if swelling appears pronounced initially.
Conclusion
Swelling after a hair transplant is an expected and manageable part of the recovery process, particularly for individuals in high-pressure academic or professional environments who seek optimal aesthetic results. By understanding the biological causes, adhering to post-operative care guidelines, and recognizing warning signs, patients can ensure a smoother healing journey. With proper precautions, swelling typically resolves within 7–10 days, paving the way for successful, natural-looking hair growth.For those considering a hair transplant—especially students and professionals preparing for international opportunities—patience and compliance with aftercare are key to achieving the best outcomes. Always consult a qualified hair restoration specialist to tailor the recovery plan to individual needs.
Related Topics